March 12, 2019 9 min read
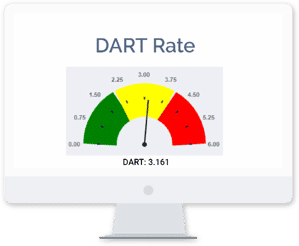
What is an OSHA Days Away, Restricted, or Transferred (DART) Rate?
Industry:
Solution:
The Days Away, Restricted, or Transferred (DART) Rate is designed to track any OSHA recordable workplace injury or illness that results in time away from work, restricted job roles, or an employee’s permanent transfer to a new position. OSHA uses the DART rate to monitor high-risk industries, and they also allow EHS managers to measure the business impact of recordable incidents over time.
How to calculate your company’s DART rate?
The DART rate is calculated using the following formula:
- (Number of OSHA Recordable injuries and illnesses that resulted in Days Away; Restricted; Transferred X 200,000) / Employee hours worked = Days Away Restricted Transferred (DART) Rate
To break this formula down, employers multiply the number of incidents that caused an employee to cease working in their normal capacity by 200,000. This 200,000 represents 100 employees working 40 hours a week for 50 weeks during a calendar year. Then, this number is divided by the total number of hours a company’s employees worked.
For example, say a company had lost-time incidents that occurred during a year. If the organization has around 1,000 employees that work 40 hours a week, this number may not be consequential or indicative of a greater problem. If, however, a smaller company only employing 10 or 15 people reports the same number of incidents, OSHA may be concerned that the company is failing to follow proper health and safety procedures.
OSHA also considers industry risk levels when examining DART rates. For example, if a logging company or intensive manufacturer has a relatively high DART rate, this may be attributed to the dangerous working environment. However, if a high rate comes from a low-risk retailer or manufacturer, this may be a sign that the organization needs to take serious steps to address this problem.
Numerous organizations throughout North America rely on Vector EHS Management Software to calculate and track DART and other incident rates.
Our best-of-breed indicators will save you valuable time and effort in monitoring safety performance metrics. Learn how we can help.
Safety KPI Guide
With so much data available, where do you start? Learn which key performance indicators you should track to monitor your safety program.
Download
What’s the Difference between the DART rate and TCIR?
A DART Rate stands for “Days Away Restricted or Transferred” Rate and includes only those OSHA recordable injuries or illnesses that resulted in days away from work, restricted duty, or transfer of duties.
The Total Case Incident Rate, also known as the TCIR and TRIR, is defined as the number of all work-related injuries per 100 full-time workers during a one-year period.
Typically, your organization’s DART rate will be lower than its TCIR. This is because only the more severe OSHA recordable injuries and illnesses are included in your DART rate.
For help with determining whether an incident is OSHA recordable, check out our ultimate guide to OSHA recordkeeping.
The Ultimate Guide to OSHA Recordkeeping
Download Now
How are incident rates used?
Incident rates serve as a benchmark that you can use to compare and evaluate your company’s safety program against other organizations or your performance in past years. It’s a good idea to keep an eye on these metrics as they play a key role in improving safety performance.
As incident rates are used throughout many industries, the type of industry and nature of the work is taken into account when analyzing past data. Incident rates are lagging indicators. OSHA officials state that these statistics indicate past performance and aren’t necessarily indicative of future incidents or procedures. For similar industries, OSHA may compare certain safety data of companies to others within the same business sector.
“Incident rates are used throughout many industries.”
“Although OSHA could potentially use this data for enforcement action unless incident rates are consistently high for a small company over a number of years, they will not normally target particular industries or companies for enforcement action,” New Mexico Mutual, a provider of medical benefits for injured workers, explained in a report.
What is a good DART rate?
DART Rates differ from industry to industry; with certain industries having a significantly higher risk than others. Many organizations compare themselves to other organizations with the same NAICS code to determine a good DART score. Overall, the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports a DART of 1.5 cases per 100 full-time equivalent workers for private industry in 2017.
How can safety software help?
Vector EHS’s Incidents Module helps companies gather essential incident-related data and then analyze it for trends or problems. Any range of incident, injury or illness can be tracked through this software, allowing your users to generate reliable OSHA 300, 300A, and 301 logs to keep in compliance with OSHA recordkeeping regulations. To learn more about how Vector EHS Management Software can help you generate incident rates, contact us today, or sign up for a free demo of the software.