



Storage and Handling of Corrosives
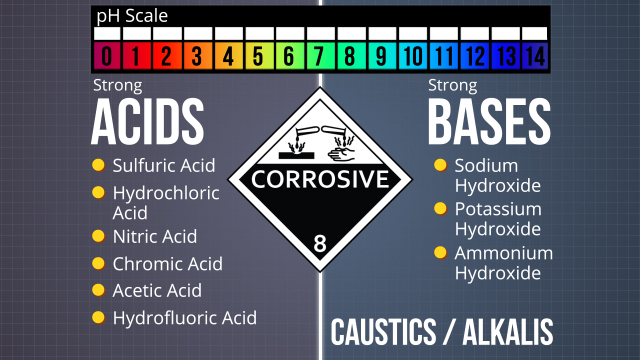
Corrosives are substances that damage or destroy other substances on contact. Most are strong acids, strong bases, or concentrated solutions of weak acids or weak bases. To safely store and handle corrosives, read the container labels and safety data sheets, and follow the requirements and precautions they contain. Also follow the storage and handling best practices for hazardous chemicals and corrosives for your workplace and listed in this course, and keep an accurate inventory at all times.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
• Define the terms “corrosive” and “corrosion” • List hazards that are associated with corrosives • Describe the requirements for workplace chemicals in OSHA’s HazCom Standard • List the information included in labels on chemical containers • List storage and handling best practices for hazardous chemicals • List storage and handling best practices for corrosives
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video |
| Based on: | 29 CFR 1910 (2016): Hazard Communication Standard |
Key Questions
Is corrosion only experienced by metals?
Corrosion is degradation caused by exposure to water, air, chemicals, heat, light, electricity, or a combination of these things, and all materials can experience corrosion.
What is the HazCom standard?
In the U.S., OSHA’s Hazard Communication, or HazCom, Standard requires information on the identities and hazards of workplace chemicals to be available and understandable to workers.
Are there special shelving requirements for corrosives?
Corrosives should not be stored on metal shelves, and corrosive containers should be placed in plastic tubs or trays, which serve as secondary containment .
Should you be concerned if you see a powdery deposit on the cap of an oxidizing acid container?
This material may be explosive, so contact the proper persons, department, or agency to safely deal with the situation.
Does the HazCom Standard specify what chemical labels should look like?
No, it just specifies the information that must be included. ANSI, NFPA, HMIS, and DOT labels are used in different settings and all fulfill the HazCom Standard.
Sample Video Transcript
Additional storage and handling best practices for hazardous chemicals include: • Store minimum amounts of hazardous chemicals • Make sure signage indicates the chemicals and hazards present in each area • Maintain labels on incoming containers, date them upon receipt, and keep stock rotated • All transfer vessels and secondary containers should also be labeled to at least identify their contents • Perform annual inspections of storage areas • Do not store chemicals in chemical hoods, on the floor, on tables or benches, or near sources of heat • Store large breakable containers on lower shelves
Additional Resources
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) – www.osha.gov
- OSHA Standards – https://www.osha.gov/pls/oshaweb/owadisp.show_document?p_table=standards&p_id=10099
- OSHA Publications – https://www.osha.gov/Publications/OSHA2236/osha2236.html
- NC Department of Labor (NCDOL) – www.nclabor.com
- NCDOL Guide – http://www.nclabor.com/osha/etta/indguide/ig30.pdf
Course Applies To
Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











