



Pneumatic Basics
Pneumatics is defined as “using pressurized gases to do work.” Pneumatic systems are based on the controlled use of compressed air as a source of stored potential energy. By controlling how the air is released, the energy can be turned into movement. Pneumatics are used in handheld power tools, automatic doors, and conveyor systems. They are also used in aircraft for landing gear, flaps, and other instruments. The air brakes on buses and trucks are pneumatic, as well as some exercise machines. Typically, pneumatic systems are more flexible, less costly, and more reliable than many other types of electric motors.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
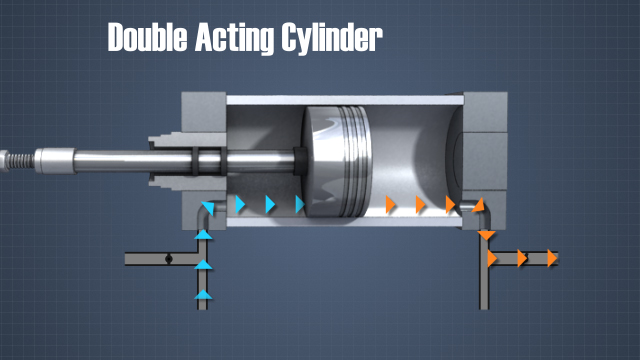
• Understand how pneumatic systems operate • Identify the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic systems • Recognize the different types of compressors, including piston, screw, lobe, and vane • Understand how to operate and maintain a compressor • Explain Charles’s law • Describe the importance of lubrication in pneumatic systems • Understand the role of pressure regulators and directional control valves • Identify the differences between single and double acting cylinders
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video |
| Based on: | Industry Standards and Best Practices |
Key Questions
What is pneumatics?
Pneumatics is defined as using pressurized gases to do work.
What are advantages of using compressed air?
Pneumatic systems are clean and less likely to be contaminated. Air flows quickly, so rapid movement is possible. Air can be dumped to the atmosphere to isolate energy.
What are some disadvantages of pneumatic systems?
Pneumatic systems can not move extremely heavy loads. Also, if the air pressure changes, the motion can be jerky or spongy. Pneumatic systems can be quite loud.
What are the different types of air compressors?
Common compressor types include piston, screw, lobe, and vane.
Do all compressors require lubrication?
No, there are some oil-free compressors that can be used when oil can not be tolerated in the air.
Sample Video Transcript
A compressor is a machine that compresses air or other types of gases from a low pressure to a higher one. Compressors are driven by either an electric motor or an internal combustion engine. Air is drawn in from the atmosphere and compressed by pistons, vanes, or other mechanisms. The compressed air is discharged into a reservoir or tank where the pressure increases as more air is added. A pressure switch turns off the compressor when a set pressure is reached. The switch also turns the compressor back on when the pressure falls as compressed air is consumed from the tank. Depending on the system and its purpose, the pneumatic system may also feature filters for cleaning the air and lubricants to keep equipment moving smoothly.
Course Applies To
Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











