


Lubrication Basics
Whenever two moving, solid surfaces contact each other, there is friction which creates heat and leads to destructive wear. Lubrication is the process of introducing a lubricant substance between the surfaces in order to reduce that friction and wear. A lubricant can be a solid such as molybdenum disulfide or Teflon; a semi-solid, such as grease; a liquid, such as oil; or even a gas such as air. This module will focus primarily on the industrial uses of liquid oils and grease as lubricants.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe the purpose of lubricants
• Identify the benefits of lubricants
• Describe the importance of proper lubrication
• Describe the key characteristics or properties of lubricants
• Describe the composition of lubricant types
• Differentiate between liquid lubricants and greases
• Describe typical factors considered when selecting a lubricant
• Describe typical methods and systems for applying or using lubricants
• Identify safety hazards and safe work practices associated with lubricants
• Describe environmental hazards associated with lubricants
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English, Portuguese, French, Polish, Russian |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video |
| Based on: | Industry Standards and Best Practices |
Key Questions
What is the cause of friction?
When two surfaces try to slide against one another, the interaction of the irregularities of the two surfaces causes a resistance to motion, or friction.
What is the purpose of a liquid lubricant?
A liquid lubricant reduces the friction of two parts moving against each other by providing a slippery film between the parts.
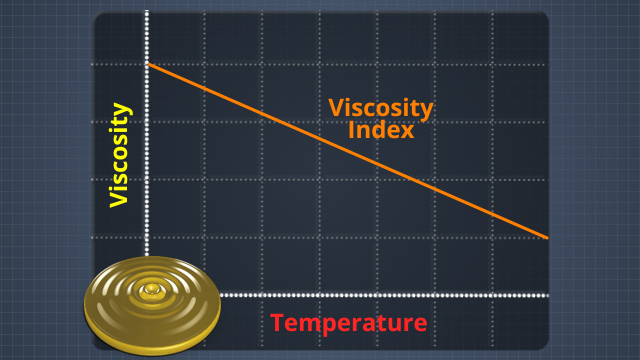
Why does synthetic oil generally outperform natural mineral oil?
At a molecular level, natural mineral oil is blend of compounds. Synthetic oil is more molecularly homogenous and can be manufactured to optimize certain performance characteristics.
What are some of the advantages that greases offer compared to liquid oils?
Grease adheres better to metal surfaces, it resists leaking from enclosures, and protects from corrosion by providing a sealing action.
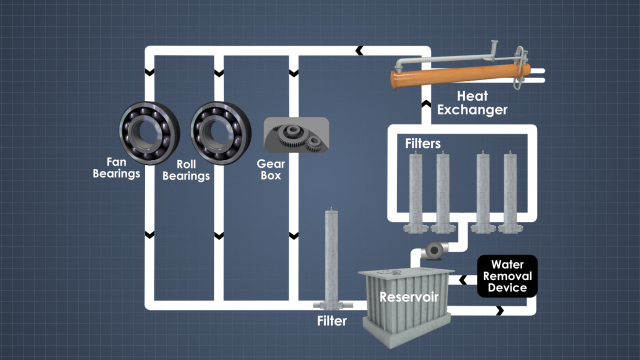
In addition to providing lubrication, what is an important function of a circulating oil system?
A circulating oil system provides the ability to remove heat from lubricated equipment. This is particularly useful for systems which experience high loading and generate a lot of heat.
Sample Video Transcript
No matter how smooth a metal surface might appear, at a microscopic level, the surface is a collection of irregular ridges and valleys. When two surfaces, for example, two metal faces of a journal bearing, try to slide against one another, the interaction of the two surfaces causes a resistance to motion or friction. If sufficient energy is supplied, the two surfaces will move relative to one another. But, in doing so, particles from the highest ridges on both surfaces will break off. The initial breaking and the damage done by the resulting loose particles moving between the surfaces translates into a overall wearing of the parts. The energy put into this destructive motion also causes the surfaces to heat up. The generated heat will accelerate the wear and lead to a failure of the parts.
Course Applies To
Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











