



Lean Manufacturing: Kanban
Did you know the word “Kanban” is of Japanese origin and translates to “billboard” or “signboard”? It is one of the Lean methodologies used to reduce wastes, such as waiting, overstocking, overproduction, and excess motion in a production process. It ensures parts are finished exactly when they are planned to be without interruptions caused by a lack of raw materials. This interactive online course provides an overview of the Lean manufacturing tool Kanban. Kanban uses visual signals to communicate the need for raw materials or parts only when there is a demand for them. This ensures that you only produce what customers want when they want it.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
- Define kanban
- Identify the qualities of a pull system
- Describe how to use kanban
- List the benefits of implementing kanban
- Describe how to implement kanban
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video |
| Based on: | Industry Standards and Best Practices |
Key Questions
What is kanban?
It is the correct methodology to follow when solving problems and managing changes.
How many columns does a typical kanban board have?
It has at least three columns that show the required tasks for completing the project.
Where should kanban be implemented?
It is highly recommended to apply kanban to a current workflow.
What is the definition of change management?
It is the adoption of tools and techniques by personnel to ensure the desired business outcome.
What type of processes are easiest for kanban implementation?
It is easiest with stable operations that have regular customer demand, a limited number of products, and reliable raw material suppliers.
Sample Video Transcript
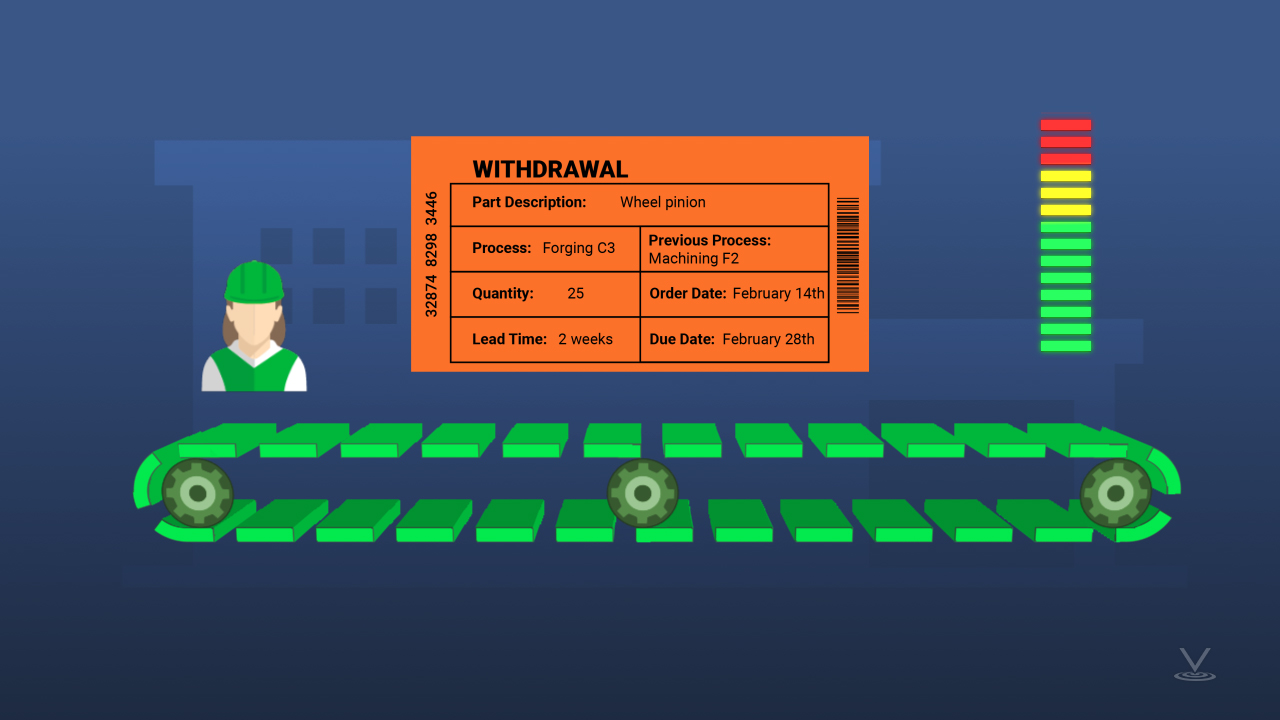
There are many other ways to utilize kanban. Project managers commonly use it to direct project activities and track their statuses. This can be done with a whiteboard and sticky notes. A typical board has at least three columns that show the required tasks for completing the project. Making it visual allows you to see the whole project and identify any potential bottlenecks. The “To Do” or “Requests” column is filled with the corresponding tasks needed for a job or project. The “Doing” or “In Progress” column show the tasks that are currently being worked on. And finally, the “Done” or “Ready for Review” column contains only completed tasks that have been moved to this column when completed to satisfaction. As you start working on each task, move the sticky note to the DOING column. If there is a task that seems to stay in this column for a number of weeks, it may be necessary to review the reason for it and adjust if necessary. Kanban doesn’t have to be done with physical cards or objects. There are many online applications and software companies that offer products to manage supplies, workflows, and projects. What may have started as manual controls for manufacturing plants, has now evolved into online applications that can be utilized by many professions. For example, Enterprise Resource Planning (or E-R-P) software is typically used by accounting, manufacturing, and logistics operations to manage inventory. Raw materials, in-process inventory, and finished goods can be labeled with barcodes or R-F-I-D tags so they can be scanned to maintain accurate inventory in an E-R-P database and trigger electronic kanban signals for withdrawing or manufacturing parts. When using software for kanban remember that it is important that the kanban signals are visible and provide clear instructions.
Course Applies To
Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











