



HAZWOPER Release Mitigation
Emergency release response actions can be divided into three main steps: 1. Identify the materials that have been released 2. Assess the severity and risk and 3. Select and implement methods to mitigate the release. Material identification and risk assessment are covered in other modules. This module focuses on the third step, release mitigation methods and their applicability.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
• Describe the steps involved in hazardous material release mitigation • List and describe various hazardous material containment methods • Describe appropriate mitigation methods for different situations
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video |
| Based on: | 29 CFR 1910.120 |
Key Questions
What is release mitigation?
Release mitigation involves containing released materials, blocking the source of the release, and decontaminating the affected area.
What is vapor suppression?
Vapor suppression is a method used to prevent a liquid spill from emitting flammable, toxic, or corrosive vapors.
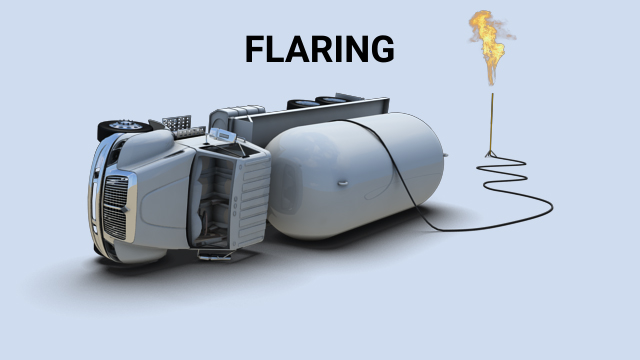
What is venting and burning?
Venting and burning is a controlled burn of flammable materials from a large tanker truck, rail car, or storage tank.
Which release mitigation method is best?
There is no single method that works for all situations. The best method depends on the type of material and its hazards. For example absorption is effective for small spills, but it is not practical for large spills because large spills can be difficult and costly to absorb.
What is the difference between a dike and a dam?
Diking involves placing or constructing a physical barrier on the ground, and damming involves placing or constructing a physical barrier in a waterway to prevent or reduce the amount of contaminants from flowing downstream.
Sample Video Transcript
Release mitigation involves containing the released material, stopping material from flowing out of the container, and cleaning up the released material. The people and methods required for mitigation are chosen based on the type and severity of the release. Only properly trained personnel should be involved with hazardous material mitigation. The incident commander is ultimately in charge of deciding which actions to take.
Additional Resources
Course Applies To
Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











