



Gear Drive Basics
Gears are mechanical devices, designed with teeth specifically shaped to minimize wear, vibration, and noise, while also maximizing a power transmission’s efficiency. They are able to reverse the direction of rotation, change the speed of rotation, and transfer rotation to a different axis. This course will describe the purpose, types, performance, and applications of gears.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
• Define gear trains and ratios • Identify gearboxes and performance specifications • Differentiate between gear types, including spur, helical, bevel, worm, rack and pinion, and crown gears • Identify additional gear types, including herringbone, spiral hypoid, and planetary • Define clearance and backlash • Describe the role of right angle drives • Differentiate between worm drives, double enveloping worms, and double lead worms • Describe the complications of noise, wear, and friction loss
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video |
| Based on: | Industry Standards and Best Practices |
Key Questions
What are the four types of gear trains?
The four types of gear trains are: simple, compound, reverted, and epicyclic.
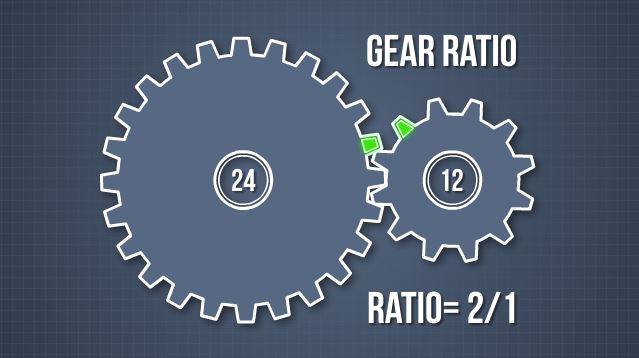
What is the gear ratio?
The term gear ratio refers to the rates at which the last and first gears rotate. To figure this ratio, the number of teeth of the driven gear is divided by the mating teeth of the driving gear.
What are the most common gear types?
The most common gear types are spur, helical, bevel, worm, rack and pinion, crown, herringbone, spiral hypoid, and planetary.
What are typical problems that can occur with gears?
A number of problems can occur with gears, including noise, wear, and friction loss.
Sample Video Transcript
Although all gears work similarly, they do come in different shapes, and configurations, and have different applications. The most common types of gears include spur, helical, bevel, worm, rack and pinion, crown, herringbone, spiral hypoid, and planetary.
Course Applies To
Demos + Pricing
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











