



Foodborne Illness: Prevention
Foodborne illness is a universal concern that affects everyone. Following foodborne illness prevention steps and participating in foodborne illness training are crucial when handling food, whether at home, in a food service setting, or in a food manufacturing facility. While eliminating all foodborne illnesses might not be possible, most cases are preventable. This course covers essential methods to prevent the spread of bacteria, viruses, and parasites during food preparation.
Request a demoCourse Details
Learning Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to:
- Identify five myths about preventing foodborne illness
- Prevent the introduction of bacterial, viral, and parasitic pathogens
- Apply cleaning standards that reduce the risks of spreading foodborne illness
- Apply the principles of temperature control to reduce the risk of foodborne illness
- Create an environment that is hostile to the growth of bacteria, viruses, and parasites
- Recognize how long prepared foods are safe
Specs
| Course Level | Intermediate |
| Languages | English |
| Compatibility | Audio, Video, MobileReady, Responsive |
Key Questions
Foodborne illness training educates employees on identifying, preventing, and controlling risks associated with foodborne pathogens, ensuring safe food handling practices in any setting.
How can foodborne illness prevention training help reduce outbreaks?Foodborne illness prevention training helps reduce outbreaks by educating workers on proper food handling practices, hygiene, and pathogen control. By understanding risks and applying safe procedures, employees can significantly minimize the chances of contamination and outbreaks.
Who should take this course?This training is ideal for food and beverage manufacturers, and anyone involved in food preparation or handling.
Is this training compliant with food safety regulations?Yes, our Food Safety Training courses provide consistent, high-quality training aligned with Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) standards, as well as FDA, Safe Quality Food (SQF), and Brand Reputation through Compliance Global Standard (BRCGS) guidelines.
Sample Video Transcript
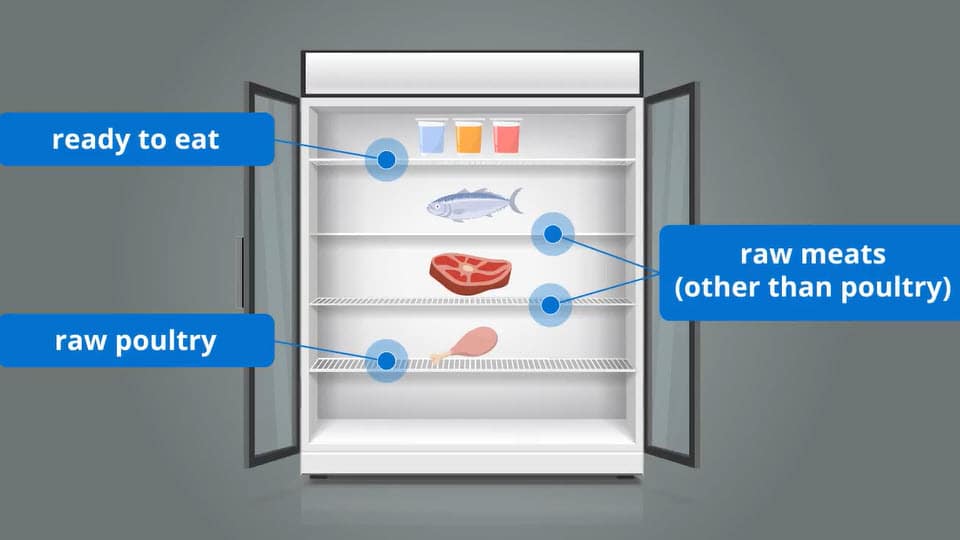
Certain foods such as raw eggs, raw poultry, meats, and seafood are known to be higher risk. Always keep raw versions separate from cooked versions. Dedicated prep spaces for these foods are essential for preventing cross-contamination. Another aspect of keeping these foods separated is to consider where they are stored in the refrigerator. Commercial refrigerators don’t have storage drawers for this reason. When storing food on refrigerator shelves: Place anything ready to eat on the top shelf. Place raw meats other than poultry on a middle shelf. Raw seafood should be placed above cuts of raw meat. Place any raw poultry, whether whole or ground, on the bottom shelf. It is the most likely to contain harmful bacteria and to contaminate other foods.
Speak to an Expert
Learn more about our courses, get pricing, and see our platform.











