December 3, 2024 6 min read

HACCP Guidelines for Food Safety
Industry:
Solution:

Employees in food and beverage production have specific food safety responsibilities. Namely, they’re required to fulfill Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) compliance requirements. But what exactly are the HACCP guidelines for food safety? And what are the seven principles of HACCP? In this comprehensive blog we’ll break down the importance of HACCP for ensuring food safety and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards, as well as provide resources for effectively fulfilling these requirements in your own organization.
What Are HACCP Guidelines for Food Safety?
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a preventive food safety approach intended to avoid the contamination of food by biological, chemical, and physical hazards.
This proactive system serves as an alternative to simply inspecting food products post-production and determining if they’ve been contaminated.
Benefits of adhering to HACCP guidelines for food safety include:
- Enhanced Food Safety: Proactively address biological, chemical, and physical hazards to ensure safer food products for consumers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet standards set by national and international food safety authorities, reducing the risk of fines or shutdowns.
- Consumer Confidence: Build trust by demonstrating a commitment to delivering high-quality, safe products.
- Efficient Risk Management: Identify critical control points, allowing targeted interventions that prevent contamination.
- Reduced Recalls and Liability: Minimize costly recalls and legal actions stemming from foodborne illnesses.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Streamline processes by focusing on critical points, leading to reduced waste and improved resource utilization.
Hazard and Risk Management Software
Explore how you can identify hazards and manage risks with powerful software designed to keep your workplace safe.
learn more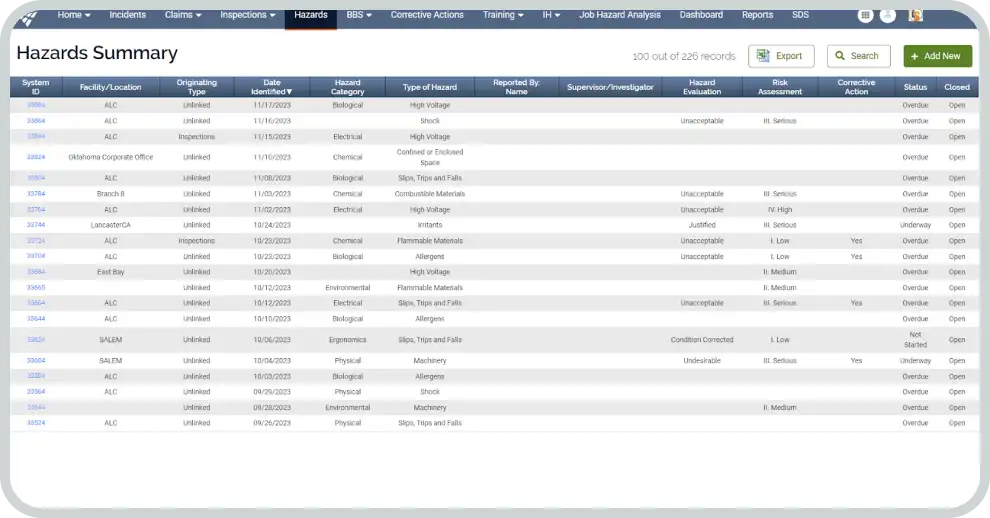
What are the Seven Principles of HACCP?
HACCP guidelines for food safety are based on seven key principles. In the following sections, we’ll break down each of these principles and provide tips for implementing them in your organization.
HACCP Principle 1: Conduct a Hazard Analysis
First, organizations should create a plan to identify food safety hazards as well as appropriate preventive measures for each hazard. Common food safety hazards include:
- Biological Hazards. This may include pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, parasites, and other organisms.
- Chemical Hazards. Examples consist of pesticide residues, undeclared allergens, and naturally occurring toxins, such as those from mold or certain plants and fish.
- Physical Hazards. This can include foreign objects such as metal fragments, glass, wood splinters, or plastic pieces that can enter food during processing. Contamination of equipment like broken machinery parts can also introduce physical hazards into food products.
- Cross-Contamination Hazards. Improper handling of contaminants and storage issues fall into this category.
HACCP Principle 2: Identify Critical Control Points
Identifying critical control points in your food production process is essential. A critical control point is a point, procedure, or step at which you can apply a control. This allows you to eliminate, prevent, or reduce the food safety hazards you’ve identified to an acceptable level.
Some common control points in food safety include:
- Maintaining proper cold storage temperatures to prevent bacterial growth
- Ensuring tools, machinery, and workspaces are free from contamination
- Conducting regular tests for contaminants, such as pathogens or allergens
- Ensuring that food packaging is intact to prevent contamination during storage and transport
- Monitoring the duration that food spends in various stages of processing to minimize spoilage or hazard risks
HACCP Principle 3: Establish Critical Limits for Each Critical Control Point
At each critical control point you’ve identified, you must determine the maximum or minimum value for the physical, biological, or chemical hazards. These limits act as thresholds that must be met to ensure the safety of the food product. If the limits are exceeded, it indicates a loss of control and a need for corrective actions.
Each organization should establish its own procedures for establishing critical limits, but this checklist can act as a helpful guide to start:
- Understand the Hazard. Review the specific hazards identified at each critical control point, then determine what conditions impact the safety of the product in relation to that hazard.
- Consult Standards and Guidelines. Use regulatory standards, industry guidelines, and scientific research to define appropriate limits. Read up on 21 CFR parts 120 and 123 for more.
- Define Measurable Parameters. Critical limits must be quantifiable to enable consistent monitoring. Common parameters include temperature, time, pH Levels, and water activity.
- Validate the Limits. Test the proposed critical limits in practice to ensure they effectively control the hazard, adjusting thresholds as needed based on real-world observations or test results.
- Document Critical Limits. Clearly record the established limits for each critical control point in the HACCP plan.
- Train Employees. Ensure all team members are trained in HACCP, its significance, and its critical limits.
Training Solutions for the Food and Beverage Industries
Equip teams with critical knowledge and keep employees up-to-date on role-specific training with Vector LMS.
Explore Now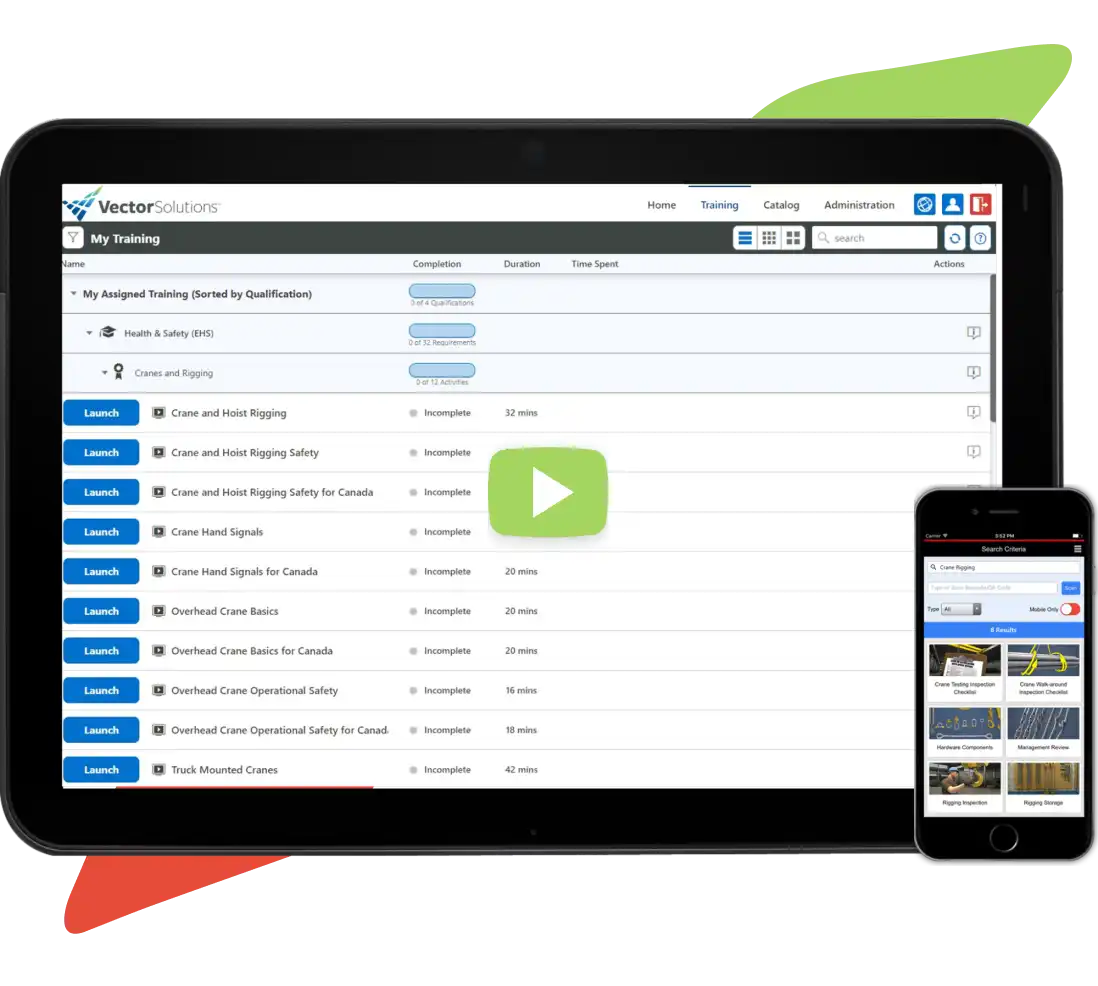
HACCP Principle 4: Establish Critical Control Point Monitoring Requirements
The US FDA requires you to document the procedure and frequency in your HACCP plan.
To ensure you’re staying within your pre-established critical limits, it’s essential to monitor conditions at each critical control point in your food production process. Make sure to document your critical control points and consistently monitor them in the workplace.
HACCP Principle 5: Establish Corrective Actions
If there’s a deviation from your critical limits, you’ll need to implement corrective actions.
At this step of the HACCP process, determine the actions to be taken in each instance a critical limit is not met. These corrective actions should ensure that no product would injure a person’s health or be otherwise adulterated if the deviation does enter commerce.
HACCP Principle 6: Establish Procedures for Ensuring the HACCP System is Working as Intended
You’ll need to create a process to validate that your HACCP program is working and that you’re producing a safe food product.
Validation can include:
- Reviewing the HACCP plan
- Reviewing critical control point records
- Reviewing critical limits
- Performing microbial sampling and analysis.
Verification tasks are performed by both FSIS inspectors as well as by plant personnel.
Complete Guide to Passing a Food Safety Audit
This guide is designed to equip food safety teams with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complex landscape of food safety regulations and audits.
Get the Guide
HACCP Principle 7: Establish Record Keeping Procedures
Finally, create procedures to complete and store records of your HACCP processes.
This includes your organization’s:
- Hazard analysis
- Written HACCP plan
- Records documenting critical control points
- Records documenting critical limits
- Records documenting verification activities
- Records documenting how you’ve handled all deviations identified.
Now that we’ve answered the question of “what are the seven principles of HACCP,” we’ll provide resources for fulfilling this final principle in the following section.
How Vector Solutions Helps Companies Implement HACCP Guidelines for Food Safety
At Vector Solutions, we provide a comprehensive EHS Management Software to help organizations create, manage, and store records for their HACCP guidelines for food safety processes. This software offers tools to streamline compliance by enabling users to:
- Design and document procedures
- Centralize recordkeeping
- Create customizable forms
- Automate workflows
This tool will help your organization simplify compliance, enhance accountability, and maintain a robust HACCP plan.
Request a demo and learn more.








